Genetic or Biological Causes of Schizophrenia
Genetic or Hereditary Factors –
Genetic or Biological Causes of Schizophrenia : In view of disproportionate incidence of schizophrenia in family background of schizophrenics, researchers have concluded genetic factors play a role in this disorder. No specific gene for schizophrenia has been identified. Most researchers agree that the disorder has polygenic involvement.

- Twin Studies –
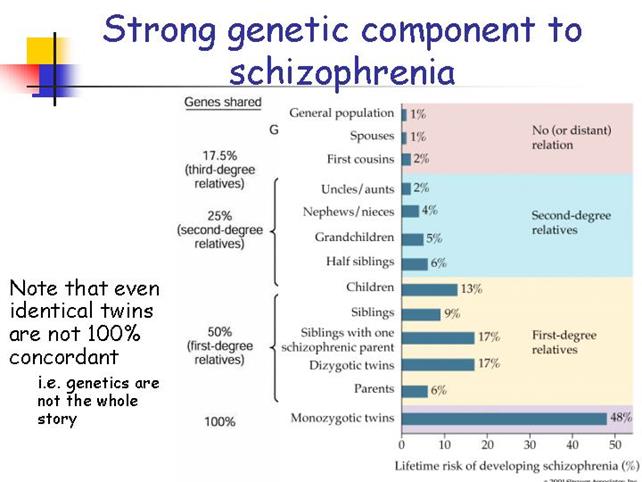
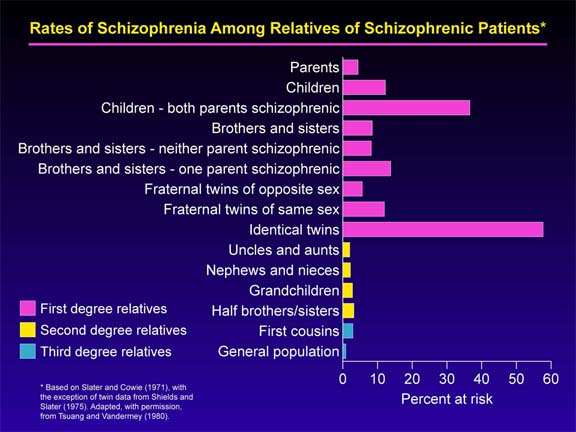
Kallmann found that the concordance rate among identical twins for schizophrenia was 86.2% and between fraternal twins was 14.5%. Torrey et al (1994) reviewed eight most adequately conducted twin studies and concluded that the overall pair wise concordance rate for schizophrenia in MZ twins 28% and in DZ twins was 6%.
Also Read: Treatment of Schizophrenia
- Adoption Studies –
Twin studies at times lack control; therefore many experts advocate use of adoption studies.
Heston (1966) was the first to use the adoption method. In a follow up study of 47 people who were born to schizophrenic mothers in state mental hospitals, but had been placed with relatives or faster homes shortly after birth. Heston found 16.6% of these subjects were diagnosed as schizophrenics. In contrast none of the 50 control subjects selected from among residents of same faster homes whose biological mothers were not schizophrenics later became schizophrenics.
Heston concluded that children born to schizophrenic mothers are not only more likely to become schizophrenic but also suffer from wide spectrum of disorders.
- Family Studies –
Heston after review of literature reported that 45% of children who have one schizophrenic parent would later become schizoid or actually schizophrenic. The corresponding statistics for children with two schizophrenic parents approached 60%.
Also Read: Types of Schizophrenia
But genetic factors cannot be sole cause because –
- The concordance rate for MZ twins is higher than that for DZ twins but never approaches 100%.
- In some studies, the discordance rate for schizophrenia in MZ twins has been found to be greater than the concordance rate.
- The higher concordance rate in MZ twins than DZ twins might be consequence at least in part of a higher rate of shared pathogenic factors other than the trained genes.
Related Topic: Psychological and Interpersonal Factors in Schizophrenia



Recent Comments